The Shockley 4-Layer Bistable Transistor Diode
- Circa 1959
Rights
Download all 3 images
PDFZIPof full-sized JPGsDownload selected image
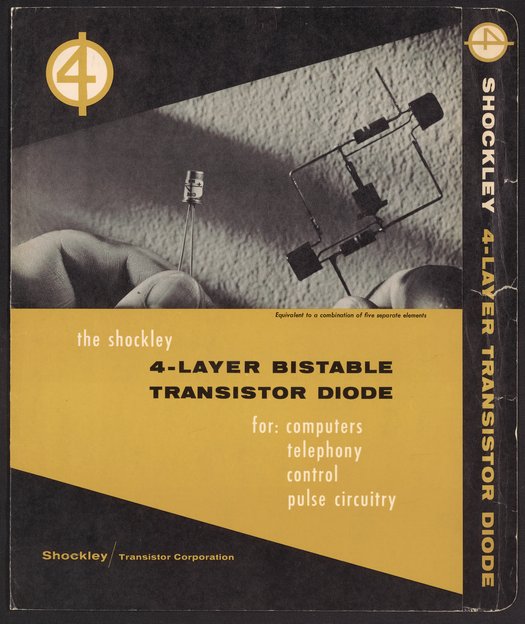
Small JPG1200 x 1426px — 294 KBLarge JPG2880 x 3421px — 1.9 MBFull-sized JPG3122 x 3709px — 2.3 MBOriginal fileTIFF — 3122 x 3709px — 33.2 MBThis brochure highlights the transistor diode's use for computers, telephony, control, and pulse circuitry.
In 1955, Arnold O. Beckman and William Shockley entered business together when they established Shockley Semiconductor Laboratories as a subsidiary of Beckman Instruments, Inc. with the goal of mass producing semiconductors.The team of scientists that Shockley assembled, however, soon grew dissatisfied that with Shockley’s management and his direction of their work towards transistor diodes and away from semiconductors. In 1957, many of them left to form Fairchild Semiconductor, which did achieve the goal of mass-producing silicon semiconductor devices and marked the beginning of Silicon Valley. Shockley did produce a new, four-layer diode, although Beckman ultimately sold the renamed Shockley Transistor Company to Clevite Transistor Company in 1960.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Creator of work | |
| Place of creation | |
| Format | |
| Genre | |
| Extent |
|
| Language | |
| Subject | |
| Rights | Public Domain Mark 1.0 |
| Credit line |
|
Institutional location
| Department | |
|---|---|
| Collection | |
| Series arrangement |
|
| Physical container |
|
View collection guide View in library catalog
Related Items
Cite as
Beckman Instruments, Inc. “The Shockley 4-Layer Bistable Transistor Diode,” circa 1959. Beckman Historical Collection, Box 97, Folder 24. Science History Institute. Philadelphia. https://digital.sciencehistory.org/works/h128nf44x.
This citation is automatically generated and may contain errors.
Rights
Download all 3 images
Searchable PDFmay contain errorsZIPof full-sized JPGsDownload selected image
-
Keyboard Shortcuts
Previous image shift + or , Next image shift + or . Pan image Zoom in + or shift + Zoom out - or shift + Zoom to fit 0 Close viewer esc Also
Mouse click to zoom in; shift-click to zoom out. Drag to pan. Pinch to zoom on touch.







